Abstract
Introduction: Allogeneic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) is a potential curative treatment for TDT. BuCy based regimen has been used widely as a standard myeloablative chemotherapy. However, the use of treosulfan based conditioning regimen has increased over the last decade (Choudhary D et al BBMT 2013). We analysed the safety and efficacy of BuCy based vs Treosulfan/Thiotepa/Fludrabine (Treo/Thio/Flu) regimens in TDT between September 2013 and March 2021.
Method: This is an observational retrospective hospital record-based study approved by Institutional Review Board. Regimen used: Treo/Thio/ Flu : Thiotepa 8 mg/kg , treosulfan 14 g/m2/day for 3 days, and fludarabine 40 mg/m2/day for 4 days . Flu/Bu/Cy/ATG : Fludrabine 30mg/ m2/ day for 6 days ,Antithymocytoglobulin 4.5mg/kg in 3 days , Busulfan (per oral) 14mg/kg ( boys) and 12mg/kg (girls) in 4 days, Cyclophosphamide 40mg/kg/day ( boys)and 50mg/kg/day ( girls) for 4 days.
Statistical Analysis: Fisher's exact test was used for discrete variables and t-test was used for continuous variables. Log-rank test was used for the difference in survival between the groups. P value < .05 was considered statistically significant. Cox regression for survival analysis was also used for time to event data of the predicted variables.
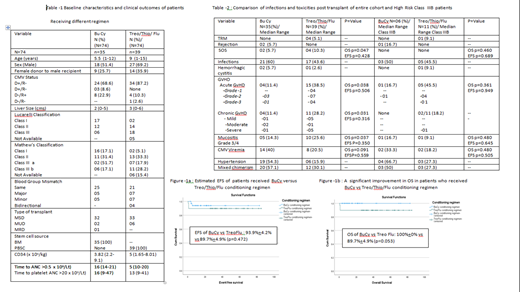
Results: As shown in Table 1, 74 patients were enrolled, out of which 35 (47.2%) patients received BuCy based regimen whereas 39(52.7%) patients received Treo/Thio/Flu. All were fully HLA matched. Median age was 5.5 (1-12) years and 9 (1-15) years respectively. According to Lucarelli classification, number of patients with Class I, II, III were 17, 12, 6 in BuCy group vs 2, 14,18 in Treo/Thio/Flu group respectively. When stratified according to Matthew classification, 06 (17.1%) and 11 (28.2%) patients were in class IIIB respectively (Mathews V et al, BBMT 2007). Source of graft was bone marrow in BuCy group vs peripheral blood stem cell (PBSC) in Treo/Thio/Flu group. Mean CD34 cell dose was 3.82(2.2-9.1) vs 5(1.65-8.01) 106/kg in BuCy vs Treo/ Thio/Flu group respectively. Neutrophils and platelets engrafted at median of 16 days (14-21) and 16 days (9-47 ) in BuCy and 15 days (10-20) and 13 days (9-41) in Treo/ Thio/ Flu. Median duration of follow-up was 28 (23-32.9) months. Two (5.7%) patients had rejection (primary=1, secondary=1) in BuCy group whereas none in Treo/Thio/Flu. Five (14.3%) vs 10 (25.6%) patients developed grade ¾ oral mucositis respectively where 1 patient in each group belonged to Class III. Sinusoidal obstruction Syndrome (SOS) was observed in 02 (5.7%) vs 04 (10.3%) patients (p=0.047) respectively, with no patients affected in Class III. BuCy group had 04(11.4%) patients with acute GVHD, including one patient with grade 3. Treo/Thio/Flu group had 15(38.5%) patients with acute GVHD including 4 patients with grade 3 which had significant impact on survival (p=0.038). We also observed chronic GVHD in 04(11.4%) and 11(28.2%) patients respectively which was mainly limited stage in former and extensive in later which impacted the survival (p=0.031). CMV viremia was observed in 14 (40%) vs 8 (20.5%) patients respectively. We also encountered significant infections in both groups {21 (60%) vs 17 (43.6%)}, however, difference was not statistically significant. Four (5.1%) patients had transplant related mortality (TRM) in Treo/Thio/Flu group, in contrast to none in BuCy group. Commonest cause of death was sepsis. Mixed chimerism was commonly seen in BuCy group {20 (57.1%)} vs Treo/Thio/Flu group {12(30.1%)}.(Table 2) At last follow up, all alive patients except two patients with rejection are transfusion independent. Five-year Thalassemia-free survival (TFS) and overall survival (OS) of entire cohort was 94%+3% and 93%+4% respectively. Estimated OS and Event free survival (EFS) of BuCy vs Treo/Thio/ Flu was 100% vs 89.7% (p=0.060) and 93.9% vs 89.7% (p=0.472) respectively.(Figure 1)
Discussion: We observed significant difference in TRM, acute and chronic GvHD and SOS favoring the BuCy group even in class III. On the contrary, we encountered rejections(n=2) and increased number of mixed chimerism in BuCy group which corroborates with previous literature (Fouzia N et al, BMT 2018).
Conclusion: In our experience BuCy based conditioning regimen is a safe and effective regimen even in high risk class III TDT, with less TRM in comparison to Thio/Treo/Flu regimen. However, one needs to be vigilant for rejections and mixed chimerism.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.